Musculoskeletal System
Musculoskeletal System (MSK), as the name suggests, consists of muscles and the skeleton. The skeleton is the framework which supports all the organs in the body. In its broadest sense MSK consists of bones, joints and surrounding structures, along with connective tissue which forms scaffolding for internal organs. Besides providing support, MSK facilitates movements of the body and internal organs.
Components of MSK
- Bones
- Muscles
- Joints
- Connective tissue
Bones provide solid support while muscles make movements of the body possible. Joints make the proper alignment of these structures. Connective tissue is responsible for support and movement of internal organs and tissues of the body.
Let us study the Joint in little more details. A typical synovial joint has following components (Fig. 1)
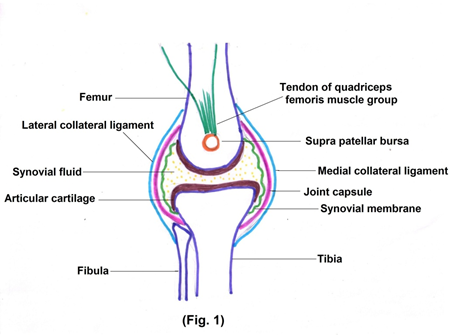
[1] Intra-articular
- Joint capsule
- Articular cartilage
- Synovial membrane and synovial fluid
- Juxta-articular bone
- Menisci and cruciate ligaments present only in knee joint
[2] Extra-articular
- Tendons
- Ligaments
- Bursae
- Enthesis
- Fascia
[1] Intra-articular
a) Joint capsule – It covers the synovial joint and separate intra-articular and extra-articular structures. It is made up of 2 layers – 1.Outer fibrous layer 2. Inner synovial membrane Joint Capsule provides strength and flexibility to joint.
b) Articular cartilage – It is smooth and slippery, which covers articular surface of bone. This highly specialized structure reduces friction between bones during movements and acts as a shock absorber. Cartilage is made up of 2 important macro molecules, type II collagen and aggrecan. Aggrecan molecules are interspersed with type 2 collagen in such a way so as to provide cushion like qualities to cartilage. Usually synthesis of the molecules and break down occurs in such a way that balance is maintained.
Articular cartilage does not have blood and nerve supply. Nourishment to articular cartilage is provided through synovial fluid. Regeneration of cartilage is not well programmed in biological system.
c) Synovium or synovial membrane and synovial fluid – Synovium, a membranous structure, covers intra-articular structures except articular cartilage and central portion of menisci in knee joint. A peculiar feature of synovial membrane is, although it lines a closed space, there is no epithelial tissue and basement membrane. Therefore, there is no barrier between synovial fluid and synovial blood vessels. Synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid. Synovial fluid is filtrate of plasma. It is a viscous fluid which reduces friction between the bones.
[2] Extra-articular Components
- Muscles – The primary function of muscle is transformation of chemical energy into mechanical energy to generate force and facilitate movement.
- Ligaments – These are fibers of fibrous capsule arranged in parallel bundles. Ligaments insert into bones on both ends. Function of the ligament is to provide stability to joints.
- Tendon also provides stability to joints. It is fibrous band which connects muscle to bone. Tendon also transmits the force of single muscle to different bones.
- Bursae – These are disc shaped synovial sacs that allow adjacent muscles and tendons to glide over each other during movement. Therefore, bursae are present in the joints when movements are relatively more. Sometimes new bursae may form in response to stress and old one may become hypertrophied.
- Enthesis – The point at which tendon is inserted into bone. In some diseases enthesis is the main site of involvement. E.g. seronegative spondylo arthropathy (SSA).
- Tendon Sheath – It facilitates gliding movement of tendon over the bone. In tenosynovitis inflammation of tendon sheath occurs, producing pain during movement of joint.
- Menisci – It is a specialized structure which is present in knee joint to give extra stability to joint. In case of injury to knee, there are chances of meniscal tear.
- Bone – It supports soft tissues and provides attachments points for tendons of skeletal muscles besides protecting internal organs. Movements of the body are possible due to bones and their alignment in the form of joints. Several minerals, especially calcium and phosphorus are stored in the bones. Hemopoiesis i.e. production of WBC, RBC etc. occur in the bones.
