Inflammation and Repair
Inflammation denotes a series of reactions set in against any injurious agent in the body, may be physical, chemical or biological and most often an infection.
It can be equated with war. Let us see what happens.
Enemy – Foreign body, unwanted matter, microbes (most common), necrotic cell, hypoxia
Army – Barriers with entries at the site, Skin and epithelia providing mechanical barriers and also produce antimicrobial substances such as defensins. Lymphocytes located at the site combat the invading agent.
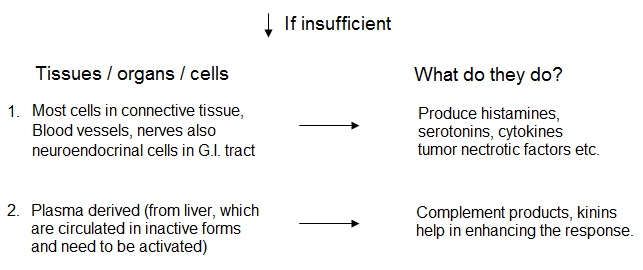
These armies of molecules interact in various ways, depending on the injurious agent, leading to different outcome of the war. If it is short lived we call it as acute inflammation.
Events in acute inflammation
Interaction between substances produced by microbes and some of the molecules mentioned earlier, produces vasodilatation of arterioles and opening of new capillaries.

Increase in protein rich fluid in extravascular tissue (exudates)

Loss of fluid and increase in diameter of blood vessels result into slow flow of blood at the site – congestion (Redness).

Leucocytes in the blood migrate to interstitial fluid, first neutrophils, then monocytes. In viral infection Lymphocytes play an important role while in allergic reaction Eosinophils participate.
Leucocytes have several receptors on their cell wall which interact with microbes or mediators like cytokines. This leads to phagocytosis i.e. killing of bacteria.
Different patterns of inflammatory reaction are observed.
- Serious inflammation in pleura, pericardium resulting into pleural or pericardial fluid.
- Fibrinous type of inflammation or in meninges or pericardium
- Suppuration can occur.
- Ulceration / fissure / fistula may be the result.

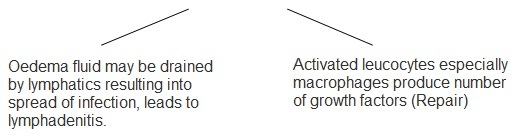
Ultimately complete resolution can occur. If tissue destruction is more, fibrosis occurs. Acute inflammation may progress to chronic inflammation.
Chronic inflammatory response
It takes various forms with tissue injury and repair processes going on simultaneously.
- Delayed type of hypersensitivity wherein granuloma formation occurs. Here macrophages are surrounded by lymphocytes just as in tuberculosis, leprosy, syphilis etc.
- Inflammatory responses may get modified by immunological component like autoimmunity or allergy.
- A tissue may get exposed to exogenous or endogenous agents leading to different kind of patterns like silicosis or Atherosclerosis.
Cells in chronic inflammation
Locally different cells participate in the process like microglia in CNS, Kupffer cells in liver, Macrophages in alveoli or Osteoclasts in the bone.
Monocytes, when activated are called macrophages which are important in chronic inflammation. Lymphocytes, eosinophils, mast cells and plasma cells also participate depending on the type of invading agent.
Repair
During the process of inflammation loss and destruction of tissue, more or less, are inevitable. As such, even normally, loss of tissue and regeneration do occur as a physiological process. Cells differ in their capacity to proliferate.
Continuous
Surface epithelial tissue, mucus membrane of the ducts, glands, cells of bone marrow and hemopoetic tissue are replaced regularly.
Stable
The level of replication is low. e.g. Parenchymal cells of liver, kidneys, vascular endothelial cells etc.
Permanent
Neurons, cardiac muscles and skeletal muscles are supposed to be permanent. However recent evidence indicates that they do have a low regenerative capacity.
Stem Cells
The replacements occur because of capacity of certain cells to proliferate and differentiate into different kind of cells. In adult, haemopetic tissue, skin and gut lining have this capacity. Another source of stem cells is embryonic tissue.
Process of repair
If damage is minor, like in surgical incision, almost original tissue is replaced. This is called healing by primary union. If damage is more, collagenous tissue is deposited and scar formation and contraction can occur. This is called healing by secondary intention. Growth factor and cytokines stimulate the process. During healing, vascularization of tissue occurs which may be pathological as in diabetic retinopathy, chronic inflammation etc. The stimulant is endothelial growth factor.
Metabolic state including nutrition, circulatory aspects like presence of atherosclerosis, hormones may affect reparative process.
Deficient scar formation may produce ulcer, excess tissue formation leads to hypertrophic scar or keloid. Contractures may result if process is not proper.
Inflammation, repair and Homoeopathic totality
Totality represents individualistic features of the disease process. The process of inflammation and repair provides a fertile ground to note down such aspects.
If nutrition is at fault, remedies like China, Calc. Phos. can be considered.
Metabolism – Sulphur, Thyroidinum
Circulation – Vipera, Hamamelis
Congestion – Aconite, Belladona
Catarrhal state – Rhus tox, Merc sol
Suppuration – Hepar. Sulph., Silecea
Ulcer, fissures, fistula – Rathania, Hep. Sulph., Silecea
The study of pathophysiology, materia medica and clinical practice should go hand in hand to explore the use of homoeopathic therapy in chronic diseases.
